How to modify environmental variables
This tutorial shows how to modify environment variables in the bash shell. Environment variables are values that affect the behavior of computer processes.
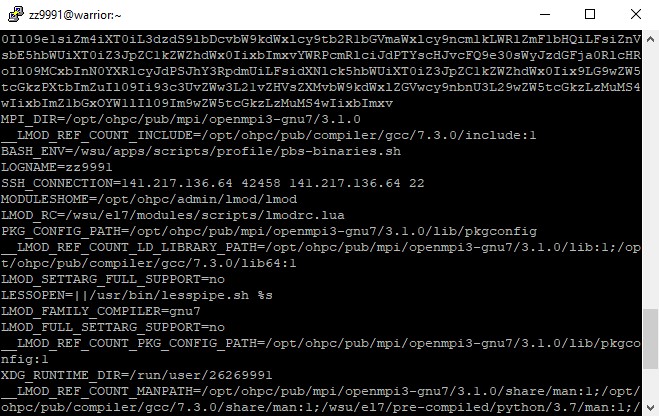
The env command allows the user to see what the current settings are for environment variables.
1. Log on to the Grid.
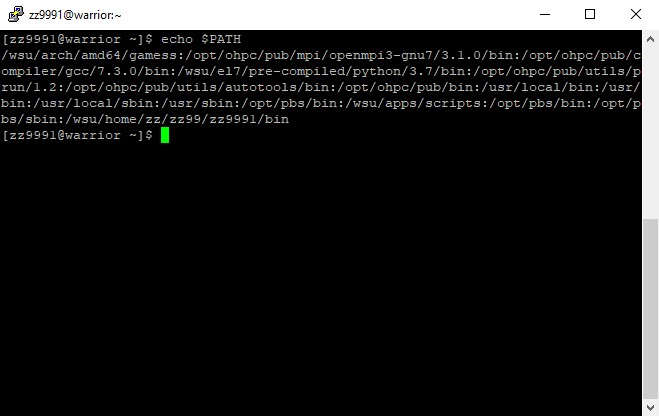
2. First, modify your $PATH. Examine your path: echo $PATH
The path will be displayed:
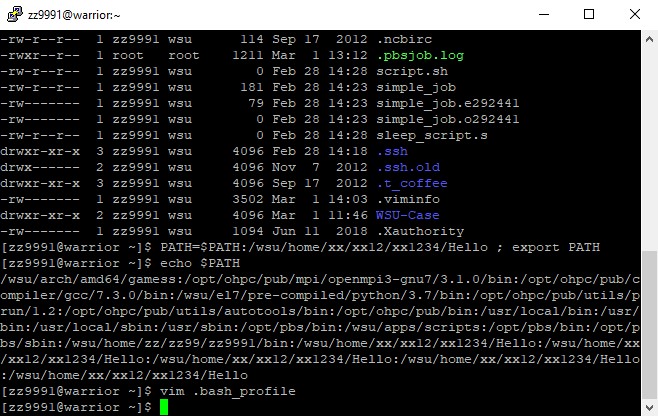
3. Check all the contents of your home directory, including the hidden ones: ls -al
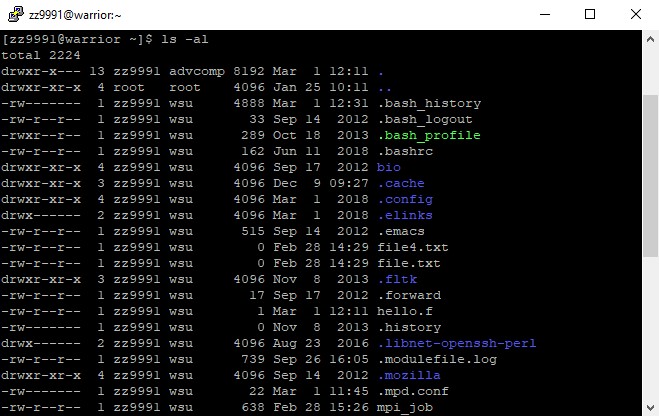
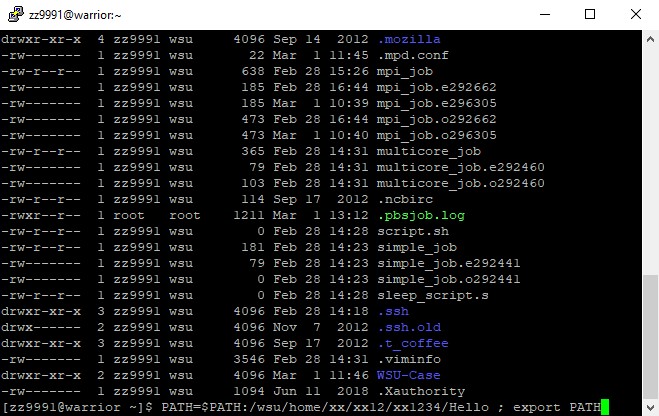
4. Select the directory you want to change your $PATH results to. In this example, we will change it to Hello. The directory 'Hello' in the user's home directory will be part of their path. Remember that this is based on your directory and not the one in the example.
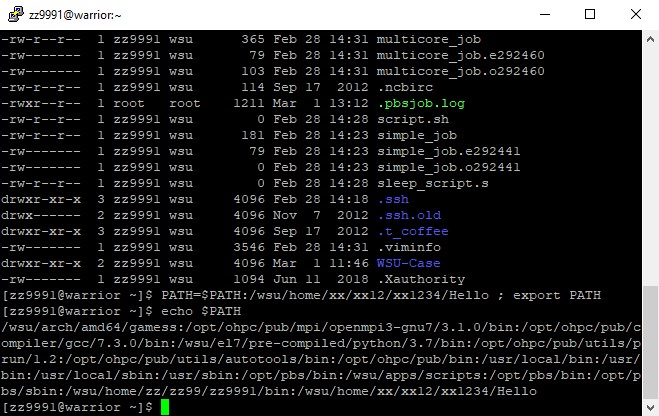
PATH=$PATH:/wsu/home/xx/xx12/xx1234/Hello ; export PATH
5. Check your path to see the change: echo $PATH
6. Your $PATH will reset each time you log on. To change it permanently, use VIM to edit the .bash_profile (this is a hidden file in your directory): vim .bash_profile
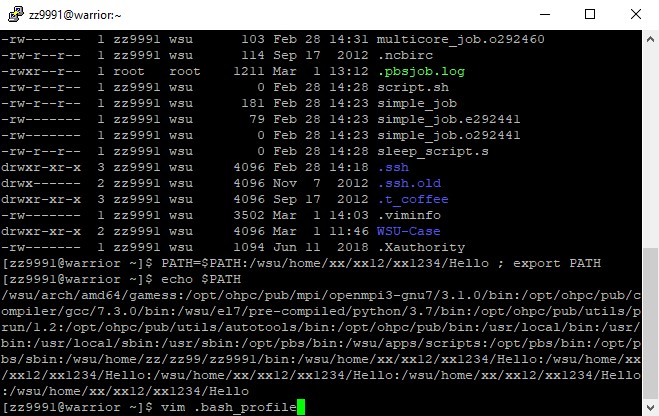
You should see a screen like this:
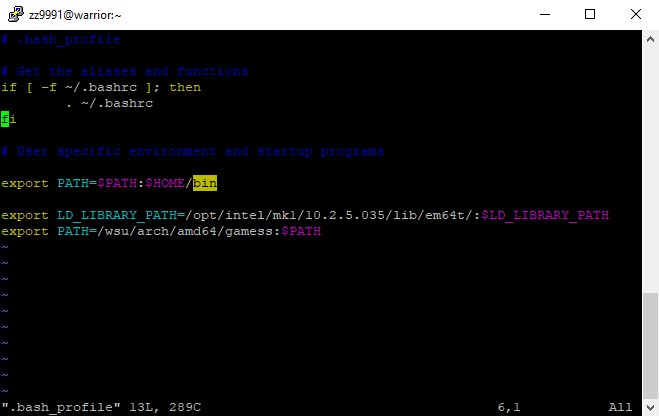
7. Change the portion under '# User specific environment and startup programs' to 'PATH=$PATH:/wsu/home/xx/xx12/xx1234/Hello ; export PATH'
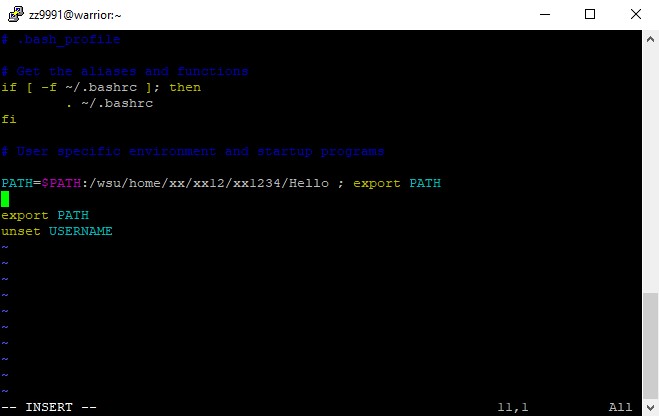
8. Save changes and quit: :wq
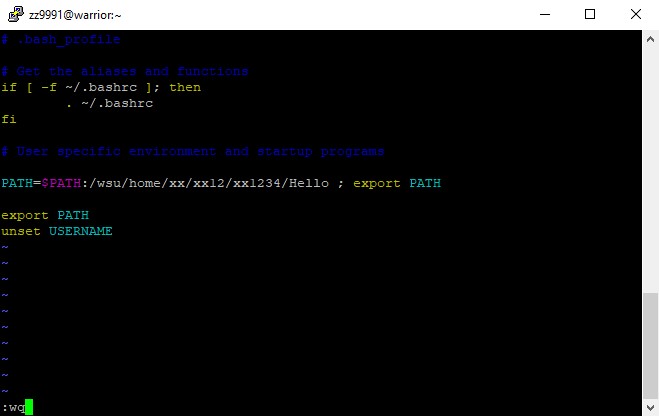
Your path should be permanently modified.
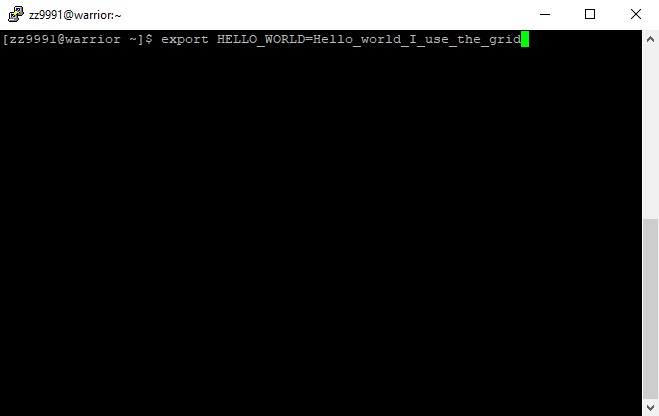
Next, here is a simple example of modifying an environment variable. We will call this variable HELLO_WORLD.
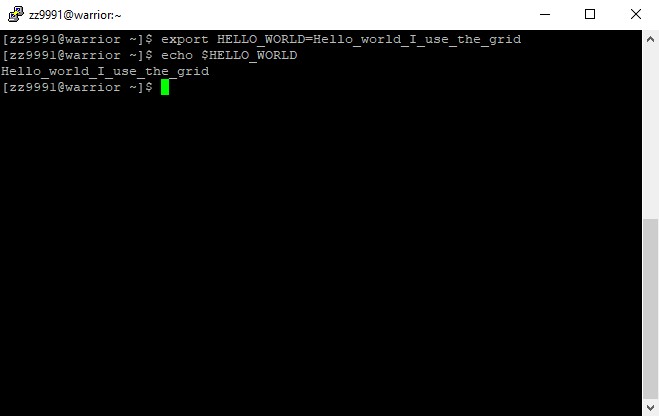
1. The name of this environment variable will be HELLO_WORLD.
export HELLO_WORLD=Hello_world_I_use_the_grid
2. Check to see the result.
echo $HELLO_WORLD
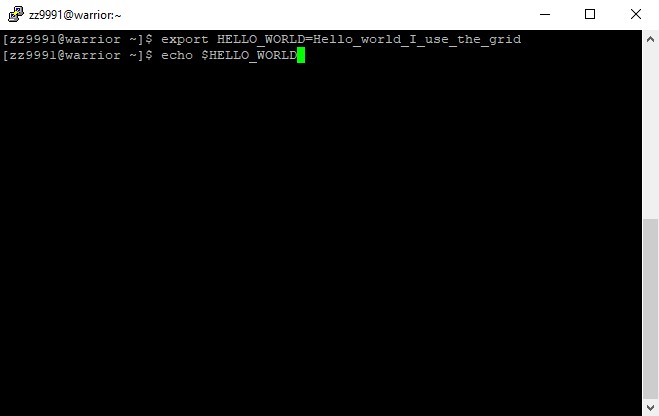
The results will display.