How to Run and Monitor Jobs for Slurm
This tutorial goes through the steps of editing a simple batch script and running it on the Grid. The job script can be used as a base to create your own batch scripts. There is also an overview of commands for monitoring and controlling jobs.
1. Log on to the Grid.
2. Copy the job script to your home directory. Type: cp /wsu/el7/scripts/tutorial/simple_job.sh .
3. The contents of the script can be viewed by typing: ls
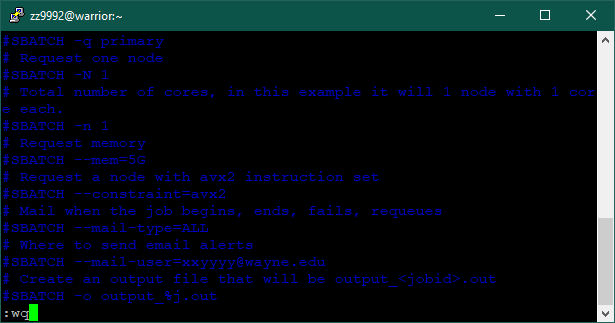
Edit the script to fit your needs. Type: vim simple_job.sh
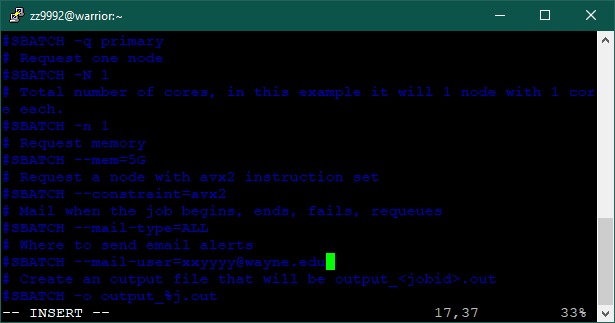
4. You are now in the vim text editor. Press 'i' to insert and edit. Use the up and down arrows to scroll through the file. Edit the email address to your own.
Press 'Esc' and then type ':wq' and press 'Enter' to save and quit.
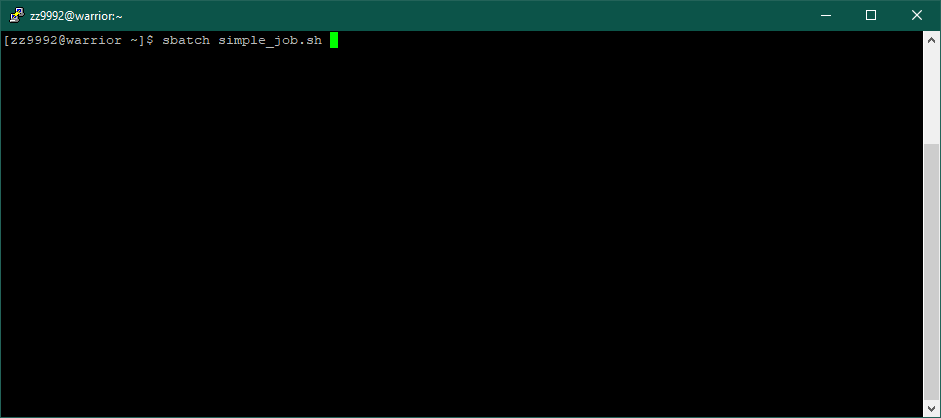
5. Now that the script is edited you can submit it to run. Batch scripts are submitted using the following command: sbatch simple_job.sh
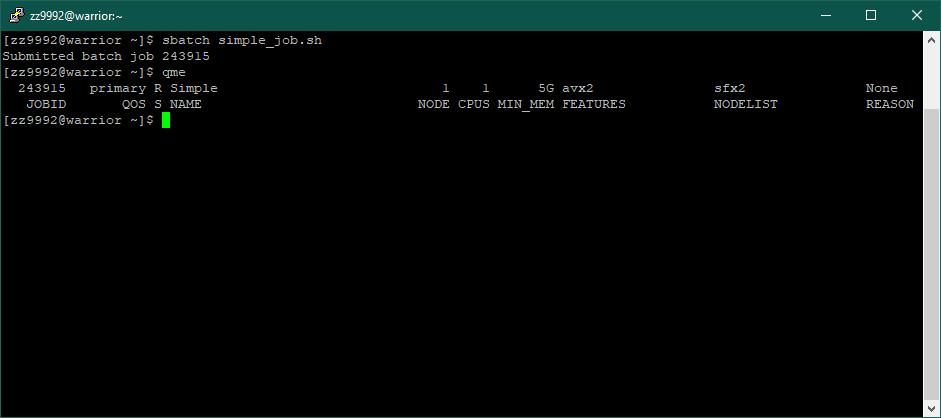
The job will be submitted and a job id will be given. In this example, the job id is '243915'. You can check the status of your jobs by entering: qme
The same can be done by using the command: squeue -u <username>
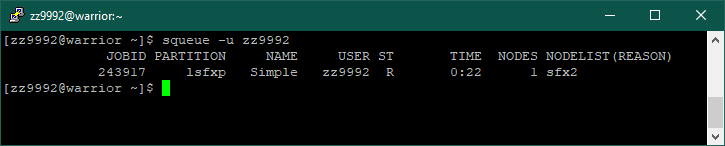
This will output the following information:
Definition | |
JOBID | Unique number assigned to each job |
PARTITION | Partition the job is scheduled to run or is running on |
NAME | Name of the job, typically the job script name |
USER | User id of the job |
ST | Current state of the job |
TIME | Amount of time job has been running |
NODES | Number of nodes job is scheduled to run across |
NODELIST(REASON) | If running, the list of the nodes the job is running on. If pending, the reason the job is waiting |
This is the various job states:
Code | State | Meaning |
CA | Canceled | Job was canceled |
CD | Completed | Job completed |
CF | Configuring | Job resources being configured |
CG | Completing | Job is completing |
F | Failed | Job terminated with non-zero exit code |
NF | Node Fail | Job terminated due to failure of node(s) |
PD | Pending | Job is waiting for compute node(s) |
R | Running | Job is running on compute node(s) |
TO | Timeout | Job terminated upon reaching its time limit |
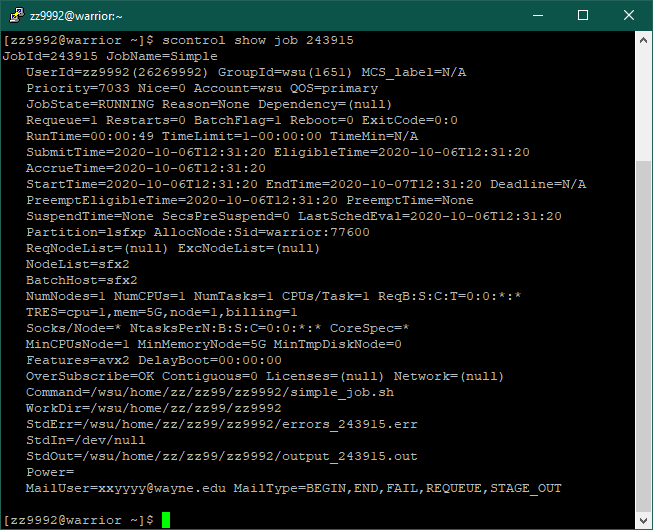
7. A useful command in getting job information is: scontrol show job <jobid>
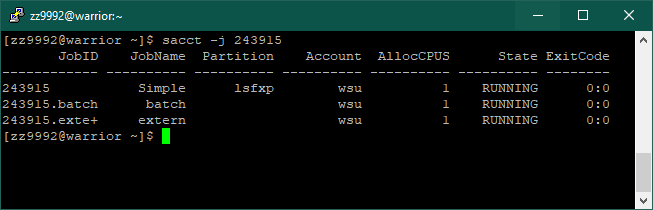
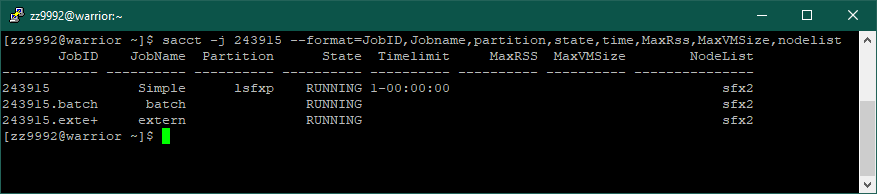
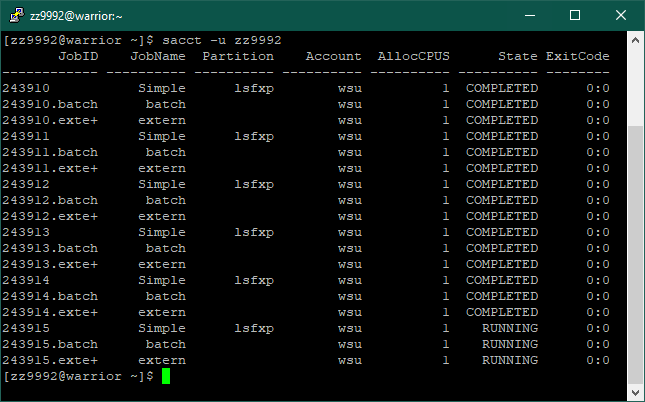
8. After your job has completed, you can get additional information using the command sacct.
Command | Meaning |
sacct -j <jobid> | Get information based on job id |
sacct -j <jobid> --format=JobID,Jobname,partition,state,time,MaxRss,MaxVMSize,nodelist | For a more detailed output add the '--format' option. Reference the man page for it here for complete options of the command. |
sacct -u <username> | View information for all jobs of a user |
9. There are a few useful commands for controlling jobs.
Command | Meaning |
scancel <jobid> | Cancel one job |
scancel -u <username> | Cancel all jobs for a user |
scontrol hold <jobid> | Hold a job from being scheduled |
scontrol release <jobid> | Release a job to be scheduled |
scontrol requeue <jobid> | Requeue (cancel and rerun) a job |
scancel <jobid>_<index> | Cancel an indexed job in a job array |